NPS Vatsalya
How to Register For The NPS Vatsalya Scheme Online
January 19, 2025
NPS Vatsalya Withdrawal Rules: Flexibility When It Matters
September 22, 2024
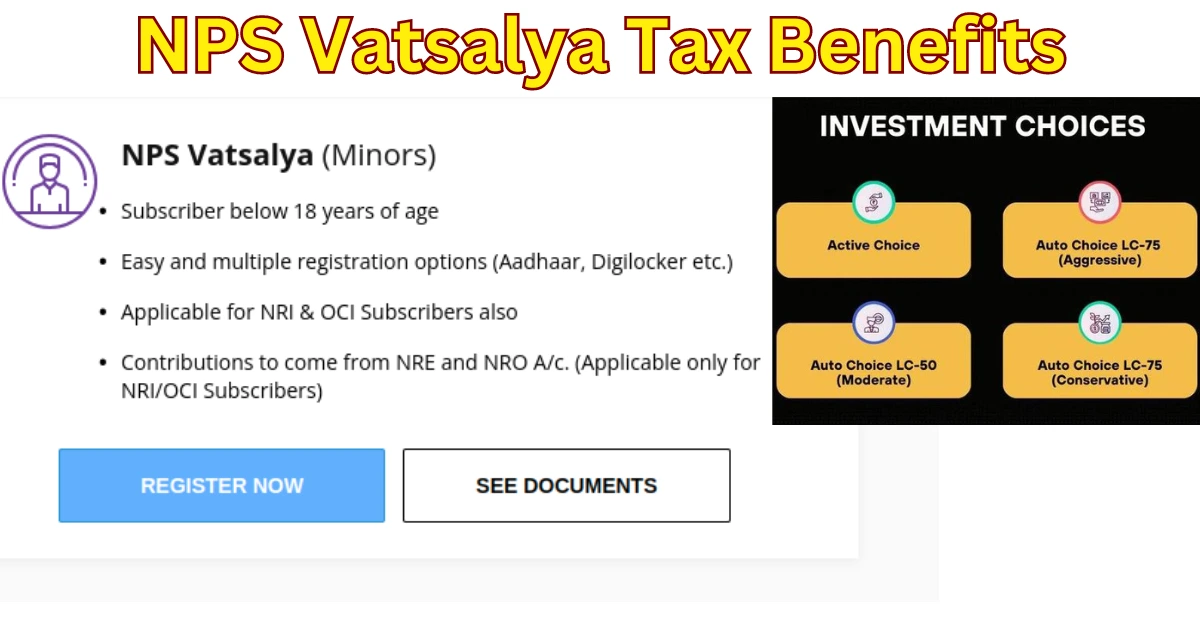
NPS Vatsalya Tax Benefits: Securing Your Child’s Future with Tax Savings
September 21, 2024
Personal Finance
Investment Outlook 2026: Where Indian Investors Stand
January 11, 2026
US Supreme Court Tariff Decision: What It Means for Indian Markets
January 10, 2026
Invest Smart After GST 2.0: Strategies for Indian Investors
September 14, 2025
Why India’s Consumption Story is an Investment You Can’t Ignore
September 13, 2025
GST Reforms: A Financial Game-Changer for India
September 6, 2025